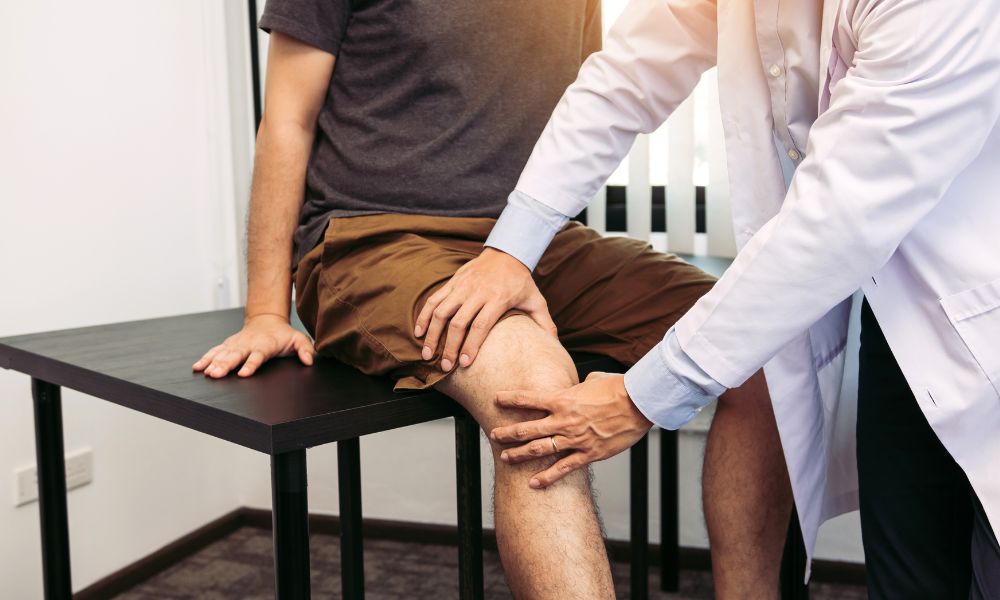
Arthritis in the knee can make everyday activities daunting. Stiffness, swelling, and constant pain can make simple movements difficult. The joint doesn't cooperate anymore the way it used to when you walk downstairs or get in and out of bed. In most cases, this disability progressively reduces the quality of one's life. That's one reason it's one of the most frustrating joint problems.
Fortunately, there is relief. You do not need to accept pain as part of aging. With the right approach, you can control symptoms and remain active with less pain. There are lots of home remedies and medical treatments. In this blog, we will discuss what is the best thing for Arthritis in the knee.
What Is Arthritis of the Knee?
Arthritis in the knee refers to the degeneration of cartilage in the knee joint. Cartilage acts like a cushion that permits the bones to move without friction. When it is absent, bones begin to grate against each other, which is the beginning of a painful experience.
You may experience stiffness, swelling, or even grinding in the knee joint. Furthermore, the knee can also become warm, sore, or tender to the touch. With time, movement becomes increasingly difficult and cumbersome, accompanied by pain.
There are a few types. Rheumatoid Arthritis is a less common form because the body's immune system attacks the joint. Osteoarthritis is the most common type, which occurs because of wear and tear, while post-traumatic Arthritis can occur due to an injury.
No matter what the reason is, the condition causes pain and immobility. Determining the cause is essential for any relief.

What Causes Arthritis in the Knee?
Arthritis in the knee develops when the cartilage that helps the knee joint function begins to wear away. There are multiple reasons for developing this issue, and knowing them can help one manage or prevent arthritis in the knee.
Age
Cartilage begins to slowly wear away as one ages. This is the most prevalent factor that leads to osteoarthritis, which is a common condition among people aged over 50.
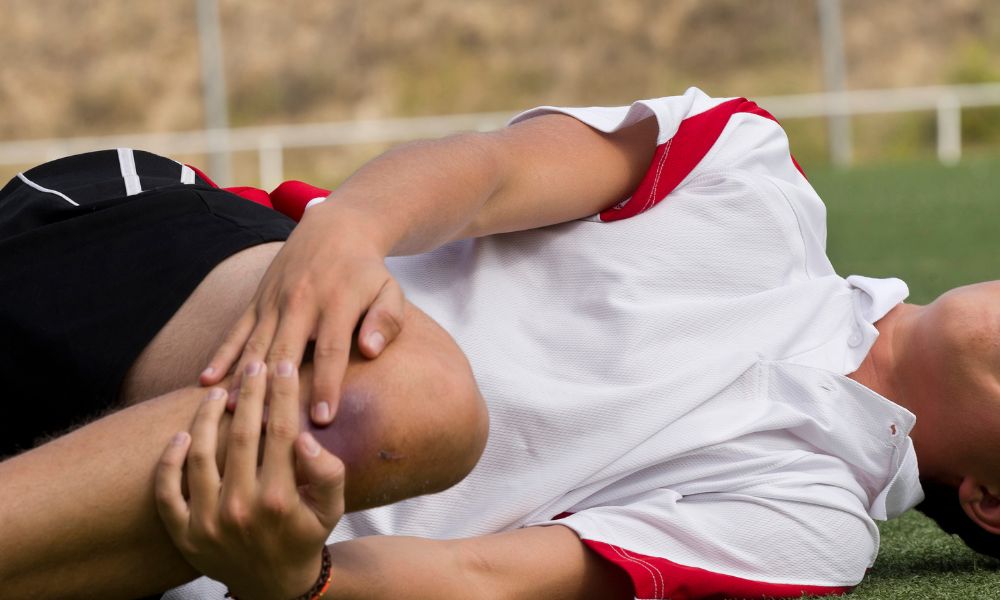
Joint Injury
Arthritis could develop from previous trauma, such as broken bones or torn ligaments. Injuries to the knee joint speed up the wear and tear of cartilage.
Overuse
Knee overexertion through activities such as running, jumping, or squatting puts excess stress that could cause damage, which will develop over time into knee arthritis.
Obesity
Added body weight increases stress on the knee joints, and most importantly, on the knee cartilage, increasing the chances of getting arthritis. Losing excess weight decreases this pressure.
Genetics
Some people might be at risk of knee arthritis due to hereditary factors. There is an increased risk if there is a family history of arthritis.
Inflammatory Conditions
Some inflammatory conditions, like rheumatoid arthritis, can predispose the immune system to attack its joints, such as the knees.
What Does Arthritis Knee Pain Feel Like?
Arthritis knee pain might differ from one person to another, but there are certain sensations that most people exhibit. Usually, it starts as a deep, constant pain that may get worse after activity or sitting for a long time.
This pain often comes with stiffness that makes movement harder, particularly in the mornings and after hours of sitting. There is also swelling around the joint, and the knee may be tender and warm.
The patient might face some knee range of motion issues in the advanced stages of the condition. Bending and straightening the joint could become a painful activity. In some instances, patients may face acute, shooting pain, particularly during standing or walking.
Increases in knee pain could lead to grinding or popping sounds where cartilage breakdown occurs, which increases the likelihood of bone-on-bone friction. Recognizing these sensations can assist in the prompt treatment or management of arthritis in the knee.
What is the Treatment for Arthritis in the Knee?
Managing knee arthritis requires a holistic approach of lifestyle adjustments, drugs, therapies, and, in some cases, surgery. The goal of each treatment is to relieve pain, restore mobility, and slow joint degeneration.
Exercise and Physical Therapy
Low-impact activities such as swimming, cycling, and walking serve to strengthen the muscles around the knee, increasing flexibility and reducing stiffness. Another benefit of physical therapy is that it can help with joint function and posture.
Weight Management
Losing extra pounds lessens pressure on the knee joints, relieving pain and helping to halt more damage to the cartilage. Even modest weight loss can make a big difference.
Pain Relievers and Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
Over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen or NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen), are helpful to manage pain and decrease inflammation. They are often the first choice in pain control.
Corticosteroid Injections
These injections place powerful anti-inflammatory medication right into the joint, providing temporary relief from pain and swelling during flare-ups.
Hyaluronic Acid Injections
In this procedure, a gel-like substance is injected into the knee joint to lubricate the joint; in some patients, this can help with movement and reduce pain.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP utilizes components of your own blood to stimulate healing in the joint. It can help regenerate tissues and ease symptoms of early-stage arthritis.
Assistive Devices
A splint, insert, or cane can reduce weight on the knee, improve stability, and provide greater mobility in daily activities.
Knee Replacement Surgery
In cases of severe Arthritis, a partial or total knee replacement may be the most appropriate choice. The surgical option involves cutting away damaged cartilage and bone, and then putting in metal and plastic components to restore the function of the joint.

What Are Some Home Treatments for Arthritis That Don’t Require Surgery?
Arthritis can be treated at home with regular exercise, without surgery. Exercise can improve joint flexibility and reduce stiffness. Low-impact activities such as swimming, biking, or yoga are good for your joints while also building strength and mobility. Using a mobility aid, such as a 4-wheel walker or cane, can provide extra support during exercise, making movement easier and safer. In addition, hot and cold compresses can temporarily relieve pain and inflammation.
Dietary changes and supplements can also help maintain joint health. For example, omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil have anti-inflammatory effects, while turmeric and ginger can reduce inflammation. Maintaining a healthy weight with these methods can reduce stress on weight-bearing joints such as the knees and hips and improve overall health.
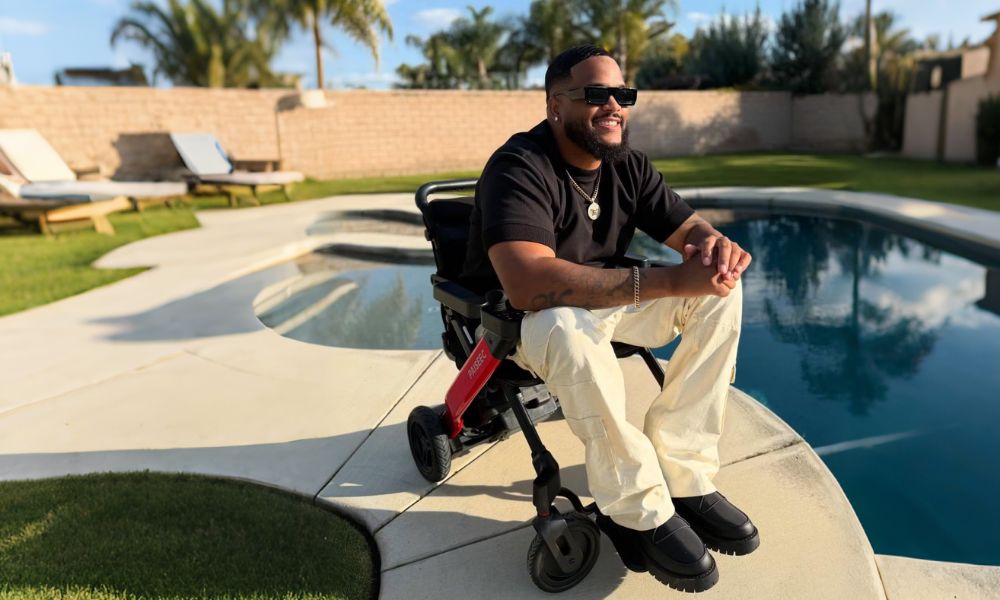
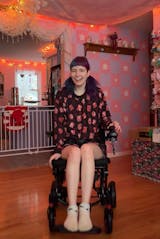
Can Mobility Aids Help with Arthritis of the Knee?
Certainly, mobility aids can be very beneficial for patients suffering from arthritis in the knee. These devices seek to alleviate stress on the affected joint, enhance equilibrium, and allow for safer movement. Common mobility aids comprise canes, walkers, electric wheelchairs, knee braces, crutches, and mobility scooters.
A cane, for instance, redistributes weight away from the arthritic knee, allowing for less uncomfortable walking. Rolling walkers offer even greater stability and are well-suited for individuals who are suffering from considerable pain or balance issues. Knee braces give compression and support, both of which can lessen irritation and realign joints. For those who have a tough time walking long distances, a 4-wheel scooter can aid in easy movement around places.
With these aids in place, the person can continue to do day-to-day activities much more easily and with less pain. It's important to speak to a healthcare provider to identify the best mobility aid that suits your condition and lifestyle needs. With the appropriate assistance, comfort, independence, and overall quality of life can improve.
What Should You Not Do If You Have Arthritis in Your Knees?
When dealing with arthritis in the knee, there are certain activities you should do to mitigate symptoms. Running and jumping are strenuous exercises that fundamentally stress the joints and accelerate the depletion of cartilage.
Avoid walking or sitting in the same position for prolonged periods, as this may result in stiffness and loss of range of motion. Avoid any movements that place additional strain on the knees, such as lifting heavy objects. Joint pain may transform into poor posture. There are also several other underlying causes that bring along pain while walking.
Ignoring pain during activities or trying to 'push through' the discomfort will slow down progress while simultaneously causing further damage. Remember to stop if your body indicates that something is wrong, and consult your physician prior to engaging in exercise. Effective knee arthritis management involves knowing what to do and what not to do.
Conclusion
Arthritis in the knee might restrict your pace, but it doesn't have to put an end to your daily activities. Simple steps and appropriate care can go a long way. Stay informed and give your body the attention it needs. However, there are many options available for relief if you look carefully. Make sure to visit a doctor if the pain worsens; professional help is the key to finding the accurate treatment for you.
Related Reading:
Can You Get a Mobility Scooter on Disability?
Which Mobility Scooter Has a Battery Generator?
What Are the Rehabilitation Exercises for Knee Pain?
How Do Tighten the Brakes on an Older-Style Black Wheelchair?
What Is the Difference Between Physical Therapy and Occupational Therapy?




















Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.